In Linux and Unix Systems, cd command is one the basic,essential and frequently use command.
Abbreviation of cd is “Change Directory” . For Linux/Unix System Administrator, it is important to know by how many ways cd command can be used. In this post, I have listed 6 examples which will help you in your daily system administration task.
Note: Directory is also known as folder .
cd command is used for changing current working directory.
cd command is shell builtin means internal command. You can verify about the shell buildin status by using type command.
What is directory
Directory is a logical section in filesystem which contains file. Directory can contain other directories which is known as subdirectory. With cd command you can move to parent directory,user’s current login directory, all directories in root directory also.
IMPORTANT NOTE : The current login user’s home directory is represented with tilda (~)
Change Directory To Currently Login User’s Home Directory
The login user’s home directory is represented with tilda sign (~) . In US keyboard, the ~ sign is available just beneath of ESC key and on the same key of backtick sign(`) . You can print ~ by pressing shift key along with backtick sign.
Syntax:
cd ~
When we use cd ~ command, users directly change to login user’s home directory.The user do not have to type absolute path to login user’s home directory.
Example:
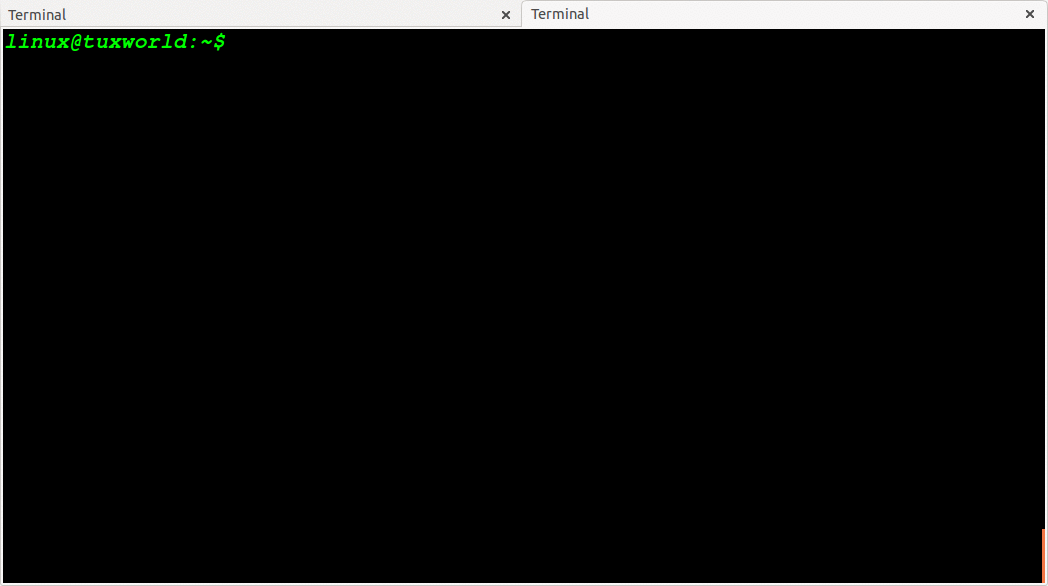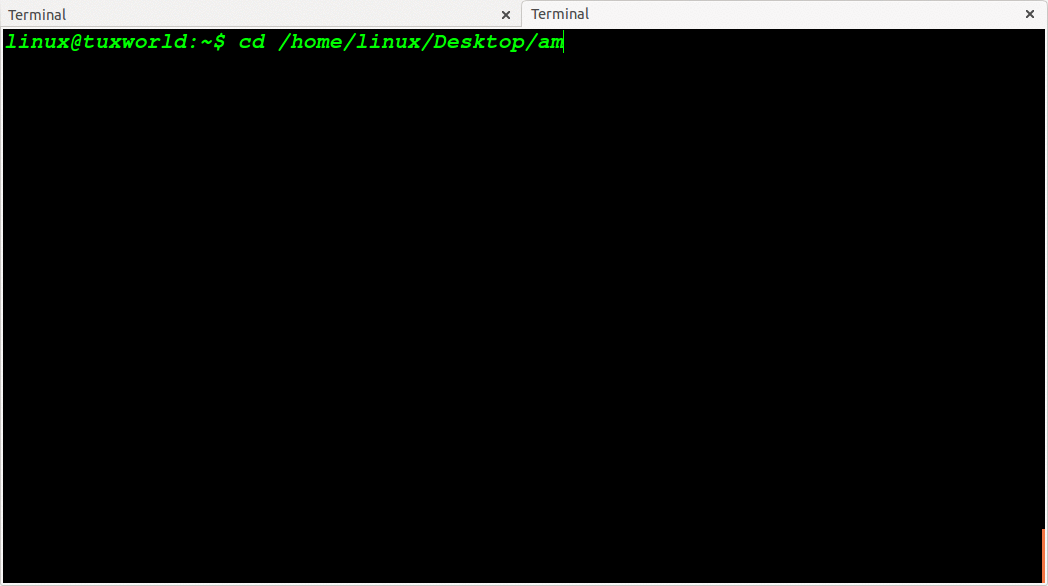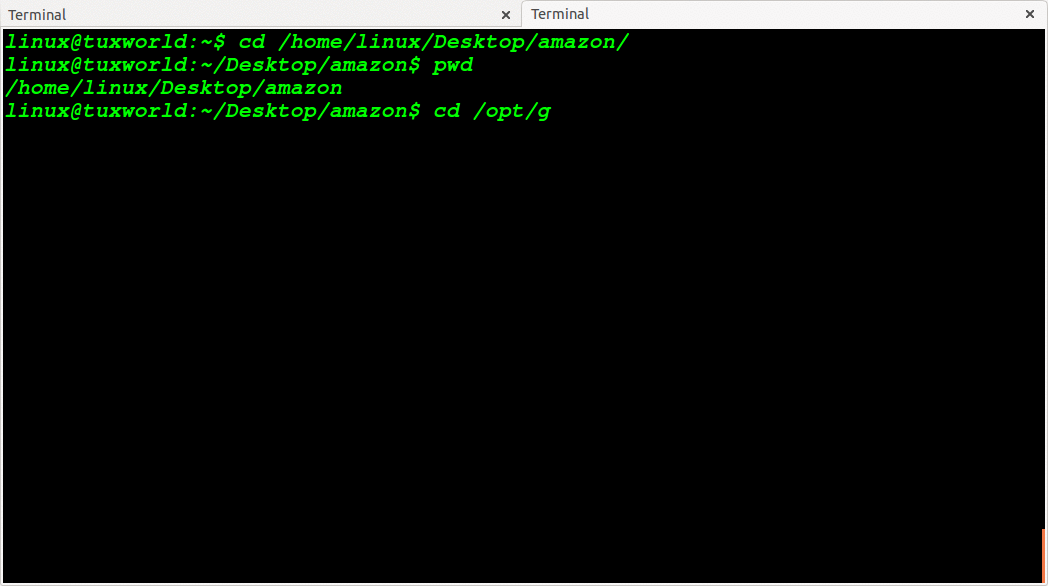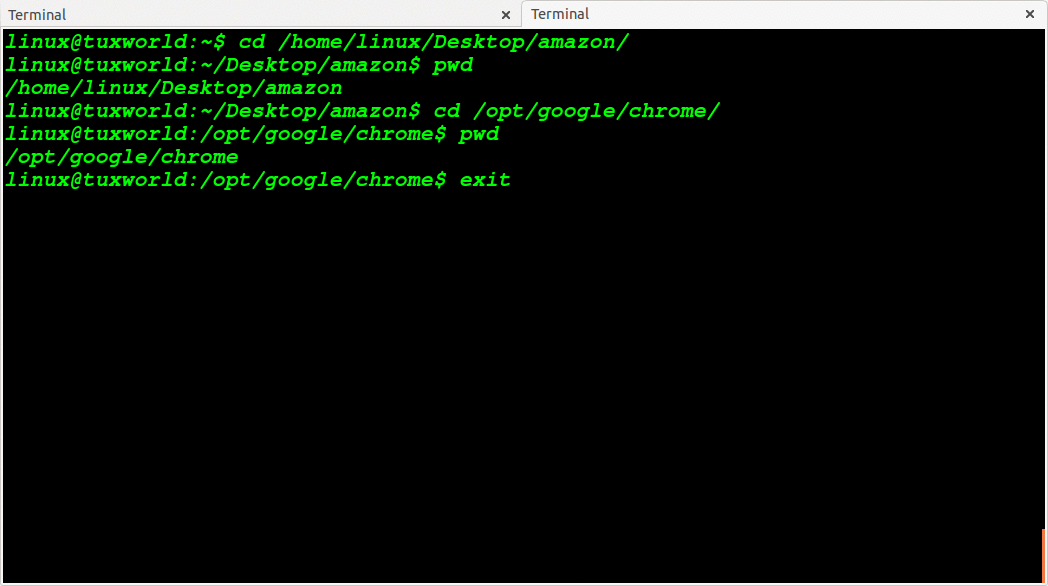
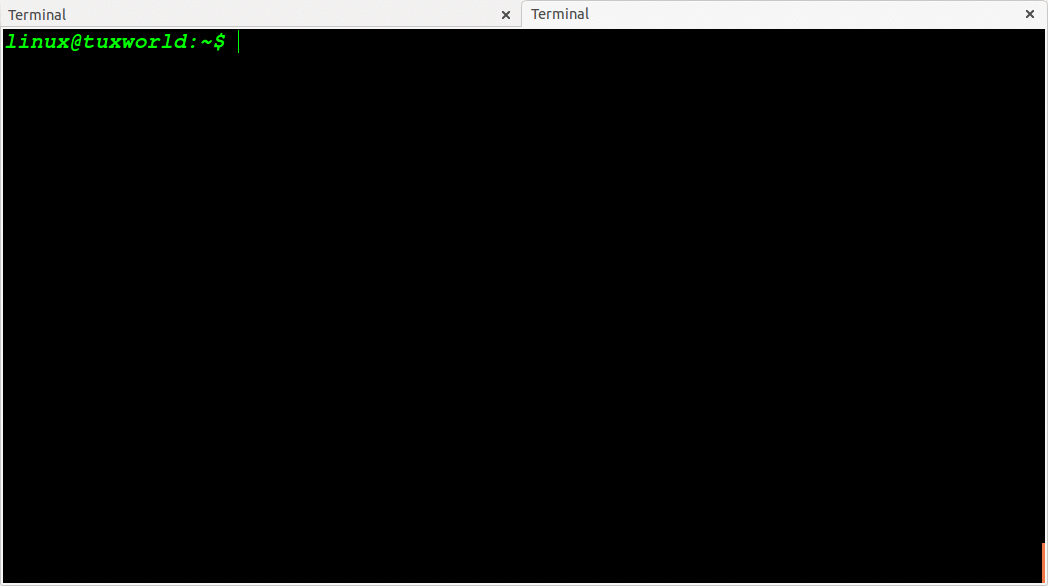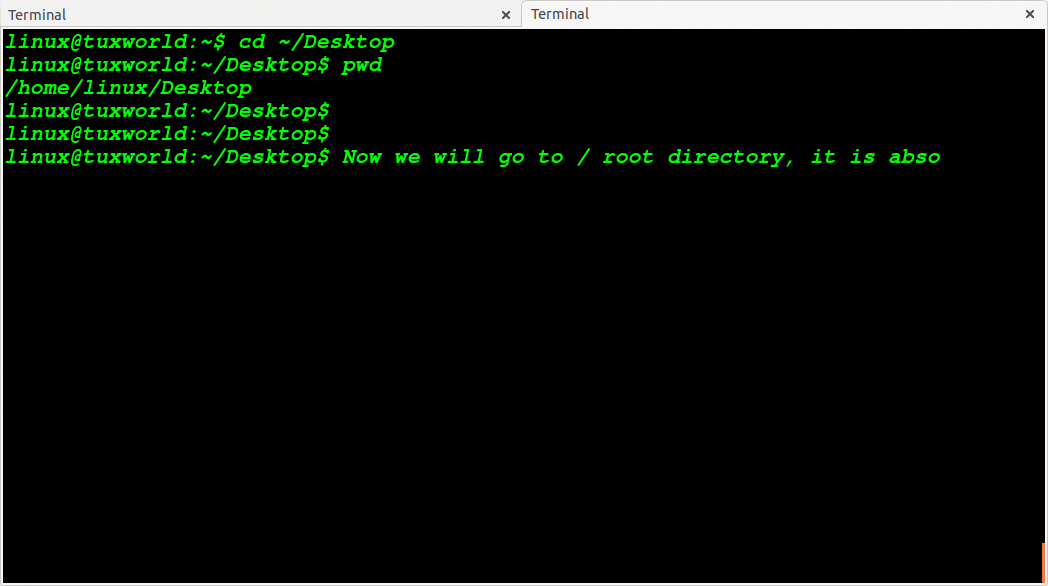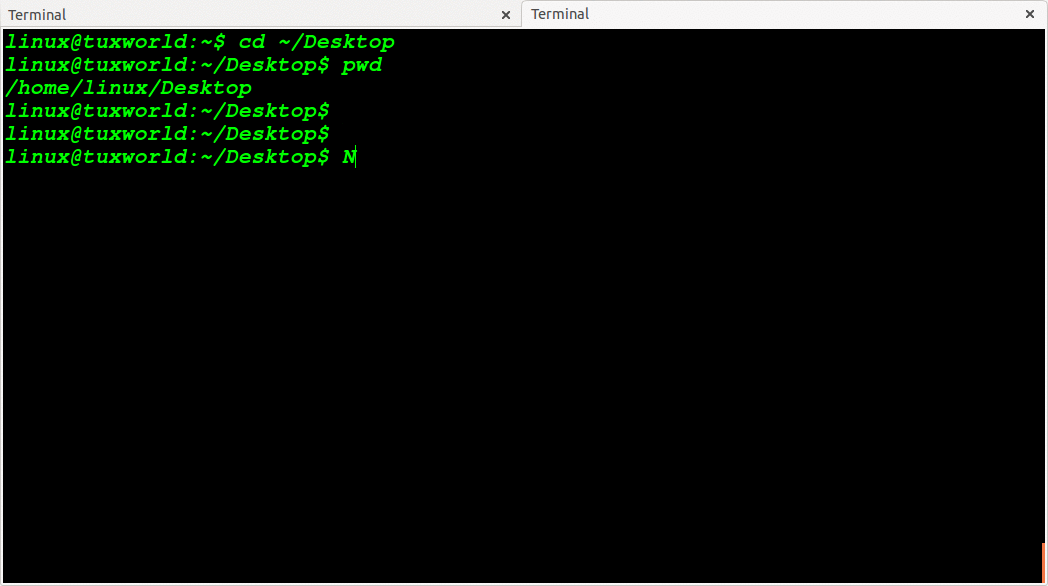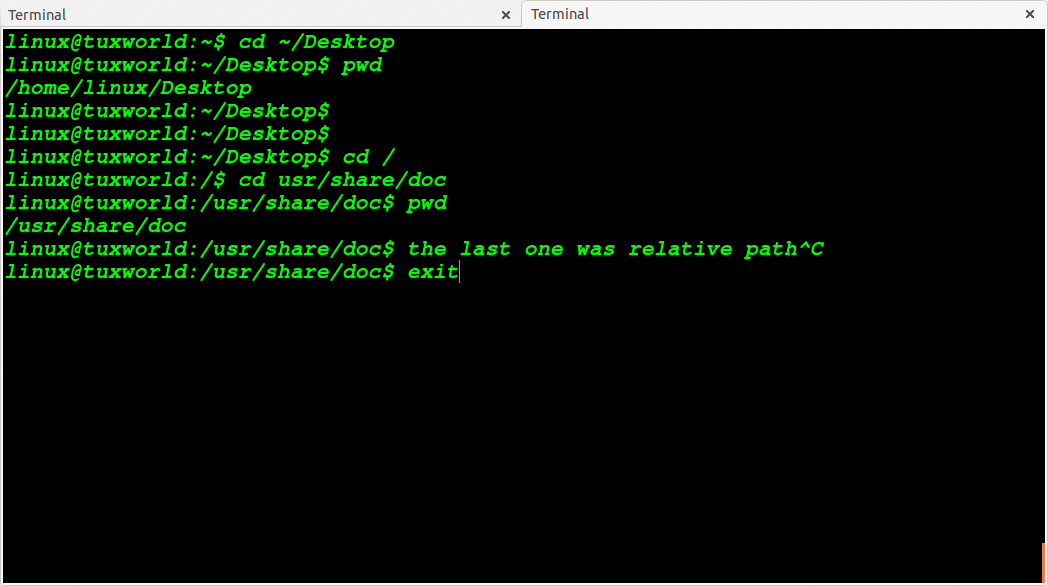
Change Directory To Absolute Path
In absolute path, the path starts with / (slash). The / (slash) represents the root directory of file system in Unix like operating system(including Linux)
For eg. See the below absolute path. In starting of path we have used / (see bolded / given below)
/opt/google/chrome
Syntax:
cd /absolute/path/of/directory
Example
Change Directory To Relative Path
The relative path meaning is when the path is started without / (slash) .
For eg. ~/Desktop , usr/share/doc
Syntax:
cd Relative/Path/To/Directory
Example:
Change Directory To Previous Working Directory
With cd command when we use the option – (hyphen) . It will move back to previous working directory from your current working directory.
Syntax
cd -
Example:
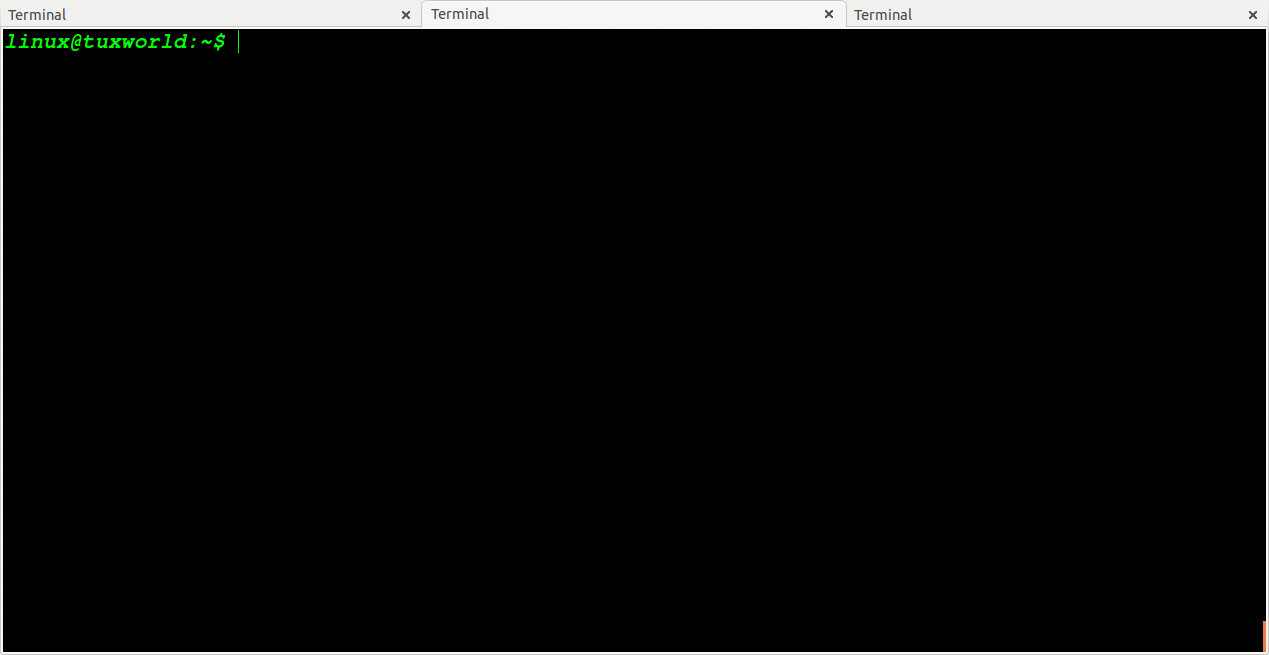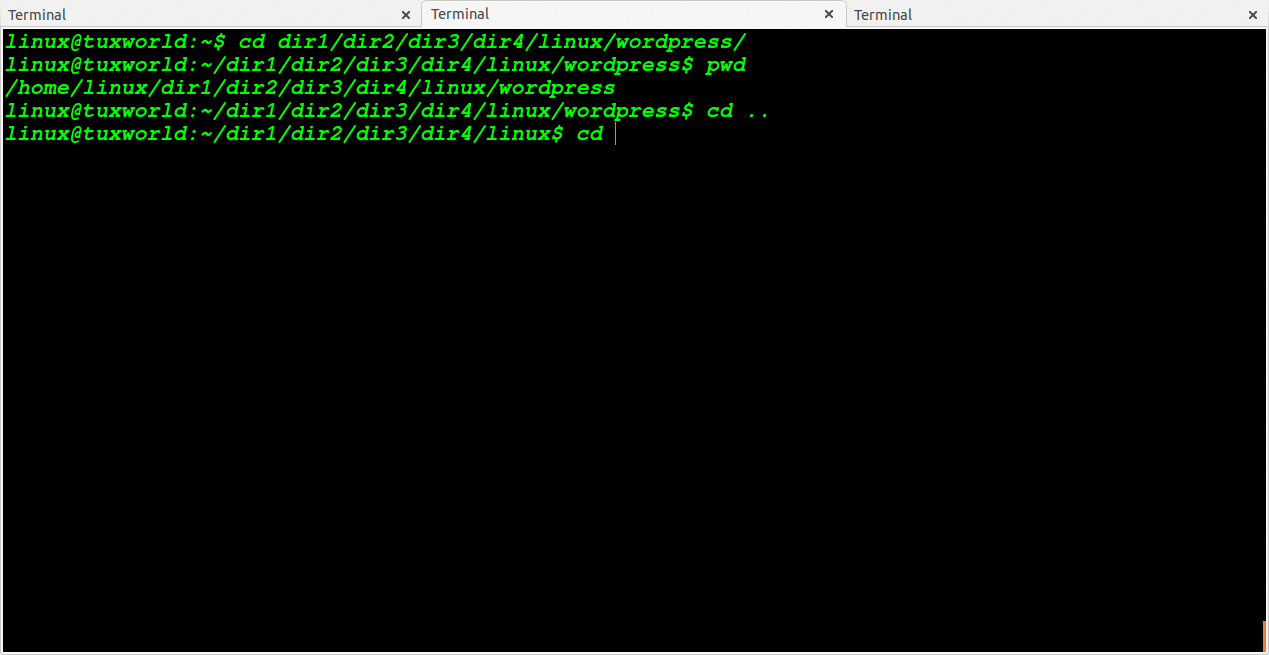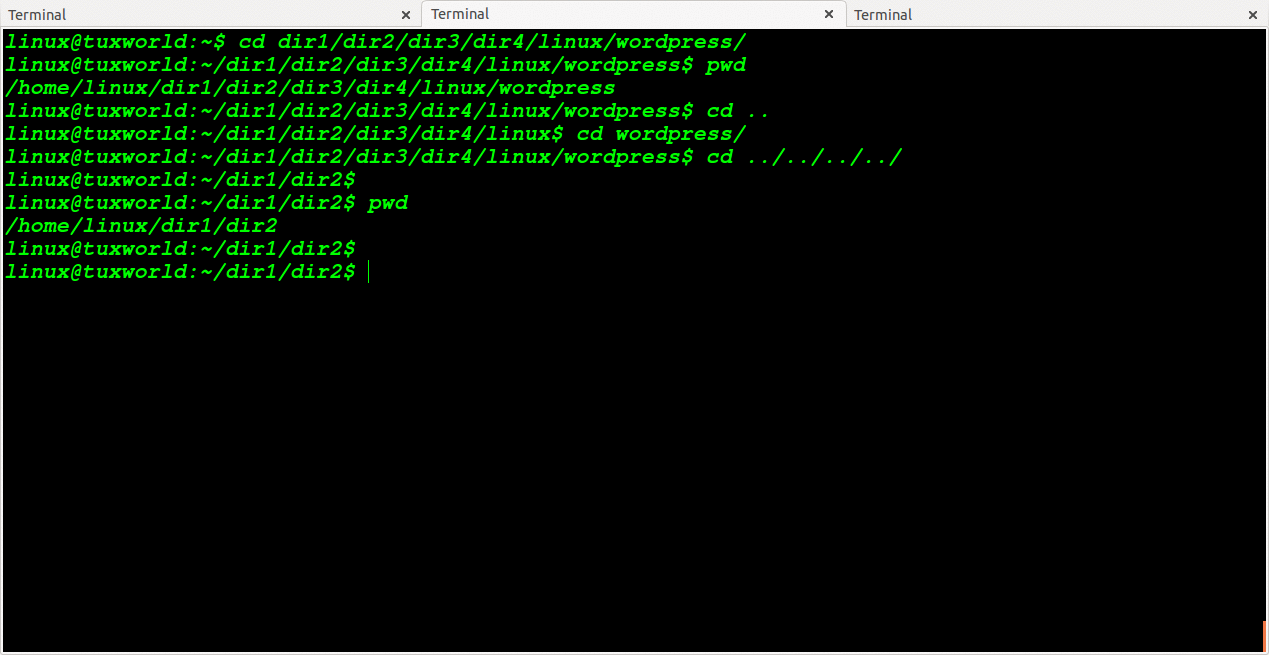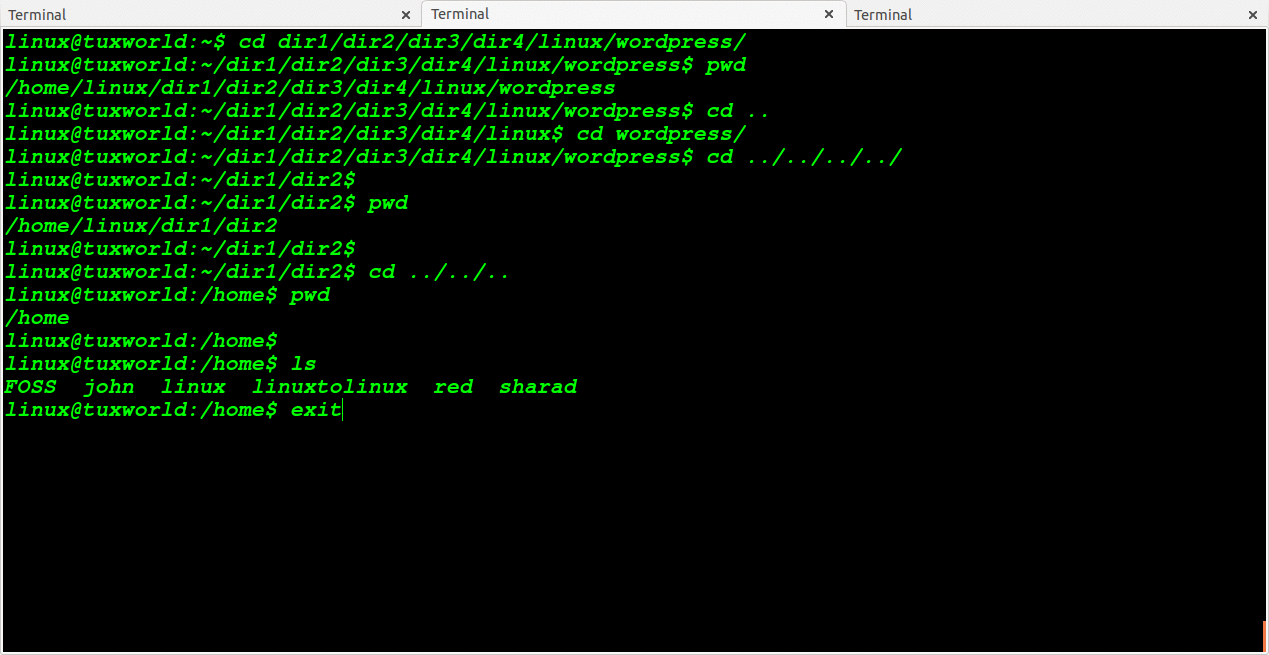
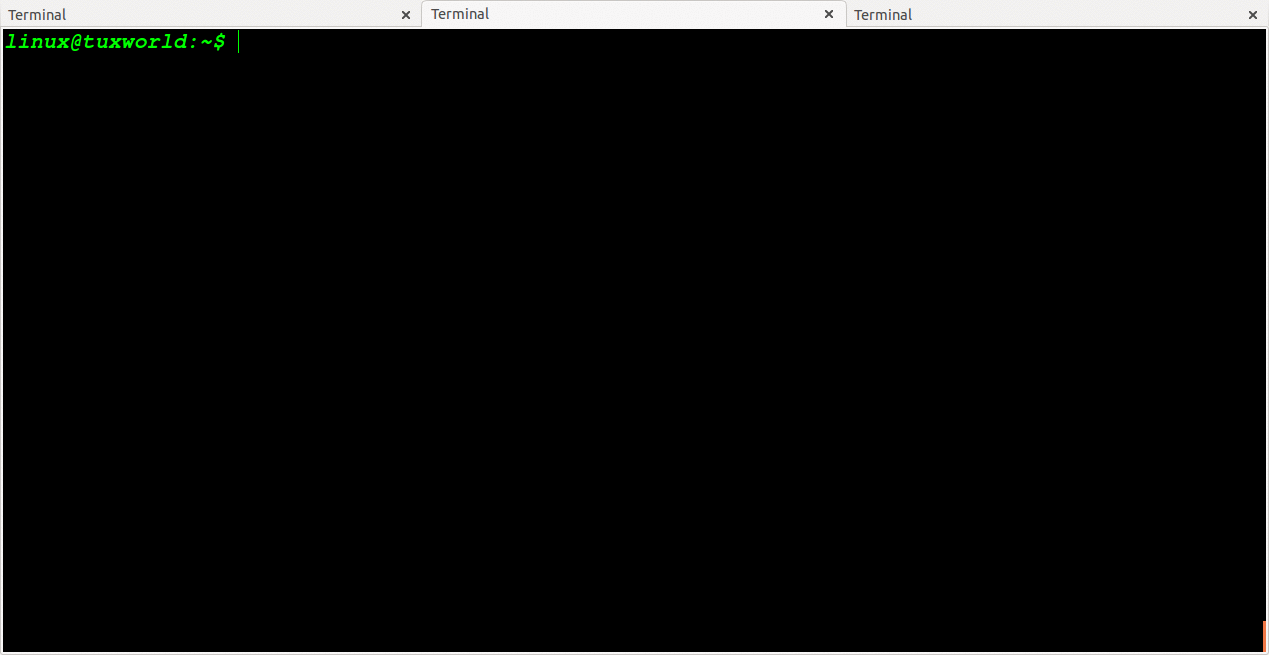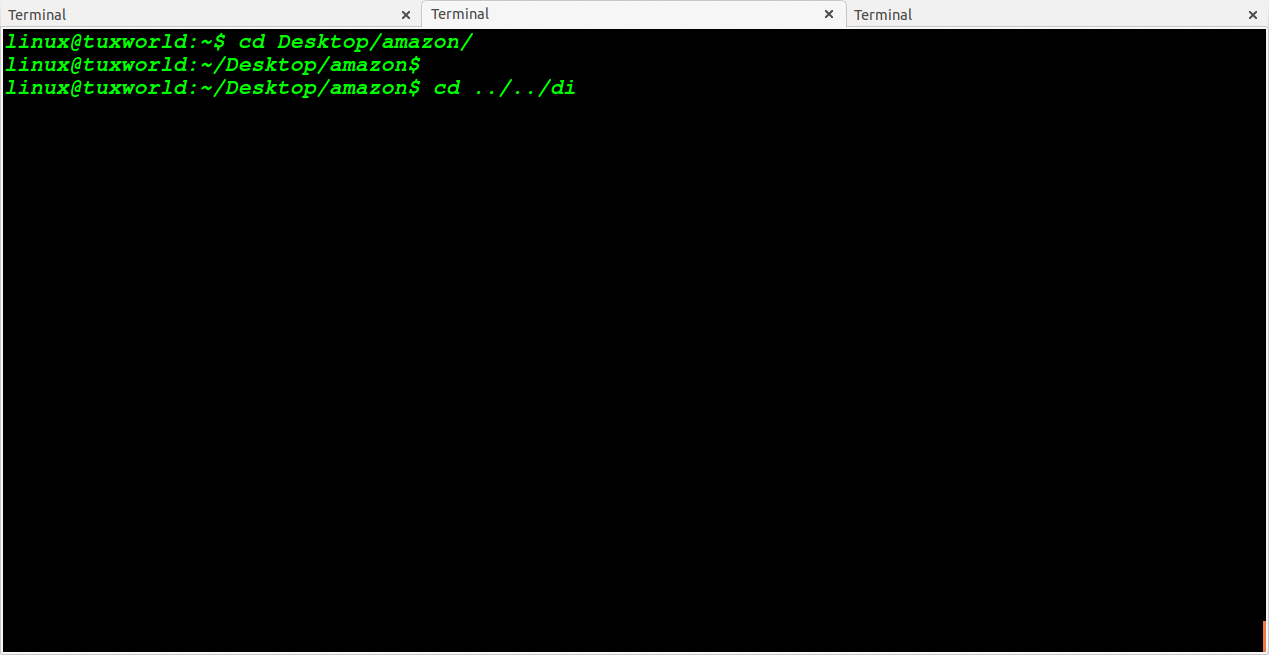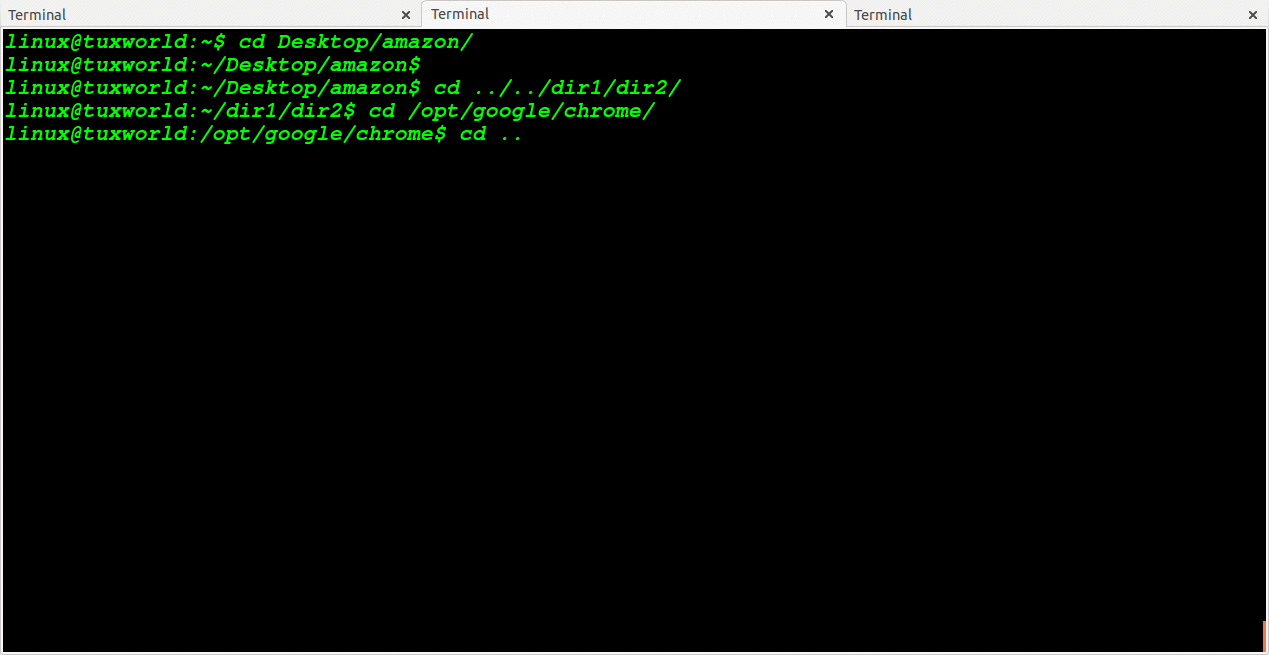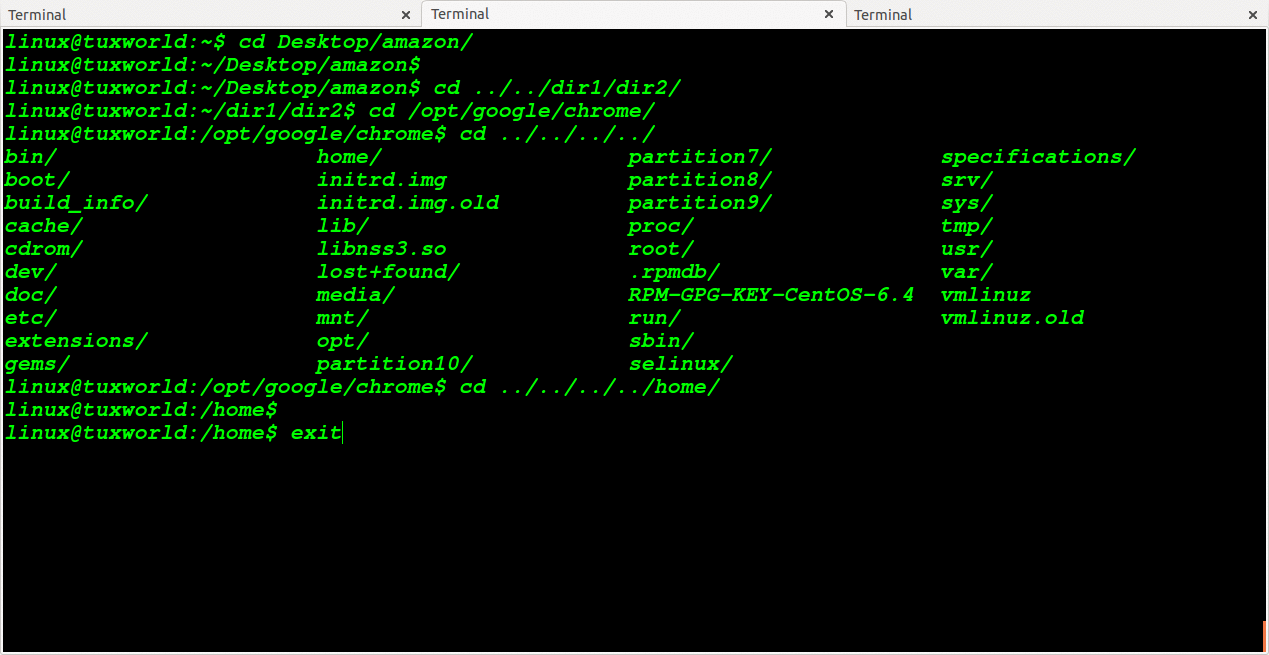
Change Directory To One OR More Level Back
To change directory to n number of level back. It is like moving back from current working directory.
To going back to one level in tree directory we use two dotes one times (..)
cd .. or cd ../
To going back to two level in tree directory we use two dots two times ( .. )
cd ../.. or cd ../../
For N number of level back, we will use N times two dots.
For 3 level back ../../../
For 4 level back ../../../../
For 5 level back ../../../../../
And Soon
Example:
Change Directory To N Level Back Then Change To Relative Path
We can change directory to some level back and move to relative path directory.
Example: